
PET Image Reconstruction
Motivation
Positron-Emission-Tomography is a functional medical imaging technique with proven utility in fields as oncology, cardiology, and neurology. By using radioactive tracers, PET allows for the detailed visualization of physiological processes at the molecular level. Our research focuses on developing new reconstruction methods and improving image quality by improving scanner calibration and normalization.
Research Topics
PET scanners are highly complex devices that demand precise calibration to achieve high-quality imaging. Although current calibration methods are effective, they can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. Our research aims to develop faster and more accurate calibration techniques that meet the stringent image quality standards required for reliable diagnostic applications.
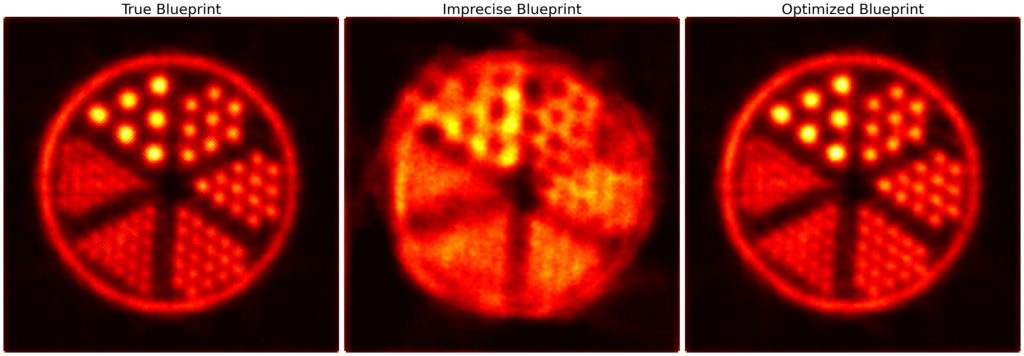
Figure 1: Reconstructions of a HotRod phantom utilizing a ground-truth, an imprecise as well as an imprecise but optimized blueprint of the mechanical detector alignment.
Additionally, the development of new hybrid PET-MRI scanner designs introduces further challenges. Since MRI does not provide linear attenuation coefficients necessary for attenuation correction, alternative methods must be employed. Moreover, due to the difficulty of fitting complex mechanical mounting and PET components within the MRI bore, non-standard scanner designs can be employed, which may result in limited angle coverage of detectors. The potential for hybrid image reconstruction under these constraints demands innovative solutions to ensure accurate and efficient imaging.
Thesis Topics
We offer various thesis topics on this project. We are looking for highly motivated and creative people with a strong background in physics, mathematics, electrical engineering, computer science or related fields. We offer an interdisciplinary working environment where you can gather hands-on experience to the field of PET imaging and image reconstruction.


